Achievements
The Fury was the first jet fighter to complete an operational tour at sea
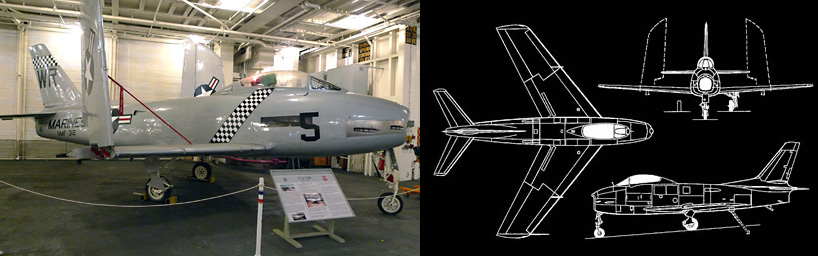
Design Features
All Moving Tailplane: Solved shockwave air compression effects as an aircraft approaches and then exceeds the speed of sound. Speed tests by the Bell-X1 & research by the British designers of the Miles M.52 lead to this critical control breakthrough. Operationally installed on the F-86E Sabrejet in 1951 & kept secret from the USSR thus delaying its use by the Soviets until 1953 with the introduction of the MiG-19.
Swept-Back Wings & Tail: Allows for supersonic speeds by delaying the onset of shockwaves. Developed by German researchers during WWII and applied famously to the transonic American F-86 & Soviet MiG-15.
Leading-Edge Slats: aerodynamically actuated at low speed to provid additional lift during landing and improved low-speed handling. During World War II German Me-262 aircraft were fitted with a version that pushed back flush against the wing by air pressure to reduce drag, popping out on springs when the airflow decreased during slower flight. The FJ-2 uses a similar design as well as the A4 Skyhawk.
Specifications on Wikipedia
Wingspan 11.31 meters (37 feet 2 inches)
Span, Wings Folded 6.89 meters (22 feet 7 inches)
Wing Area 26.75 sq meters (288 sq feet)
Length 11.45 meters (37 feet 7 inches)
Height 4.14 meters (13 feet 7 inches)
Height, Wings Folded 4.78 meters (15 feet 8 inches)
Empty Weight 5,355 kilograms (11,800 pounds)
Loaded Weight 8,525 kilograms (18,790 pounds)
Max Speed at Altitude 970 KPH (600 MPH / 520 KT)
Service Ceiling 12,700 meters (41,700 feet)
Range with Drop Tanks 1,595 kilometers (990 MI / 860 NMI)
Armament: four Colt Mk 12 20-mm cannon w/ 600 rounds



